山东科技大学 电气与自动化工程学院,山东青岛266590
快速反射镜(Fast Steering Mirror,FSM)是高精密光学系统中的关键仪器,基于音圈电机(Voice Coil Actuator,VCA)驱动的柔性支撑FSM存在复杂耦合特性,导致系统模型复杂并严重影响系统的控制性能,对于该问题,本文提出了一种基于系统辨识与模型降阶的双轴积分增广滑模控制方法。首先,采用基于脉冲响应的Hankel矩阵系统辨识方法建立VCA-FSM的精确耦合模型;随后,基于平衡实现与平衡截断,在保证模型精度的前提下对所建立的高阶模型进行降阶;其次,基于降阶模型,采用现代控制理论方法设计积分增广滑模控制器,通过设计状态观测器构造滑模切换函数与控制律,并在控制设计中改进符号函数以消除滑模抖振;最后,基于VCA-FSM伺服控制系统实验平台,开展频域与时域性能测试实验。实验结果表明:本文所提控制方法相较于单轴滑模、PID控制方法,系统的闭环跟踪带宽分别提高了约50.3%,251.3%,扰动抑制带宽分别提高了约39.9%,451.9%,阶跃响应调节时间分别缩短了约29.7%,97.7%,螺旋线跟踪精度分别提高了约48.5%,97.8%,且实现了对存在强耦合特性VCA-FSM的解耦控制。本文所提控制方法充分提高了VCA-FSM的控制性能。
快速反射镜 音圈电机 系统辨识 模型降阶 滑模控制 Fast Steering Mirror(FSM) Voice Coil Actuator(VCA) system identification model reduction sliding mode control 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(24): 3580

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Center for Information Photonics and Communications, School of Information Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 611756, China
Temperature sensing is essential for human health monitoring. High-sensitivity () fiber sensors always require long interference paths and temperature-sensitive materials, leading to a long sensor and thus slow response (6–14 s). To date, it is still challenging for a fiber optic temperature sensor to have an ultrafast () response simultaneously with high sensitivity. Here, a side-polished single-mode/hollow/single-mode fiber (SP-SHSF) structure is proposed to meet the challenge by using the length-independent sensitivity of an anti-resonant reflecting optical waveguide mechanism. With a polydimethylsiloxane filled sub-nanoliter volume cavity in the SP-SHSF, the SP-SHSF exhibits a high temperature sensitivity of 4.223 nm/°C with a compact length of 1.6 mm, allowing an ultrafast response (16 ms) and fast recovery time (176 ms). The figure of merit (FOM), defined as the absolute ratio of sensitivity to response time, is proposed to assess the comprehensive performance of the sensor. The FOM of the proposed sensor reaches up to , which is more than two to three orders of magnitude higher than those of other temperature fiber optic sensors reported previously. Additionally, a three-month cycle test shows that the sensor is highly robust, with excellent reversibility and accuracy, allowing it to be incorporated with a wearable face mask for detecting temperature changes during human breathing. The high FOM and high stability of the proposed sensing fiber structure provide an excellent opportunity to develop both ultrafast and highly sensitive fiber optic sensors for wearable respiratory monitoring and contactless in vitro detection.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(8): 1397
光电编码器检测系统的误差主要受基准光电编码器测角误差、数据采集误差、检测系统同轴误差影响。其中,基准光电编码器的测角误差可进行补偿。因此设计了一种基于极度梯度提升树(extreme gradient boosting,XGBoost)机器学习的算法用来补偿基准光电编码器的误差。经该算法补偿后,静态精度提高了35倍,标准差由3.62″减小至0.13″,最大误差值由5.53″降低至0.39″。与传统的误差反传(back progagation,BP)神经网络算法以及径向基函数(radial basis function,RBF)神经网络算法补偿效果相比,XGBoost的补偿效果更优。XGBoost机器学习算法有效降低了基准光电编码器的测量误差,提高了光电编码器检测系统的检测精度。
光电编码器 误差补偿 XGBoost 检测精度 photoelectric encoder error compensation XGBoost accuracy of detection 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(7): 20210958
光纤布喇光栅(FBG)在构成大型传感网络时,由于光源带宽有限会出现光谱重叠的问题。提出了一种人工蜂群(ABC)算法及改进ABC(IABC)算法的解调技术,结合谱形复用技术与IABC算法对光谱重叠中的各个光栅的波长进行识别,并对多个FBG传感系统进行实验仿真与分析。实验结果表明:IABC算法在多FBG传感复用系统中的解调误差不超过3.6 pm,解调时间不超过7 s,温度测量精度达0.5 ℃,解决了多个FBG传感网络部分重叠和完全重叠问题。
光纤布喇格光栅 传感网络 光谱重叠 解调算法 改进人工蜂群算法 fiber Bragg grating sensor network spectrum overlap demodulation algorithm improved artificial bee colony algorithm
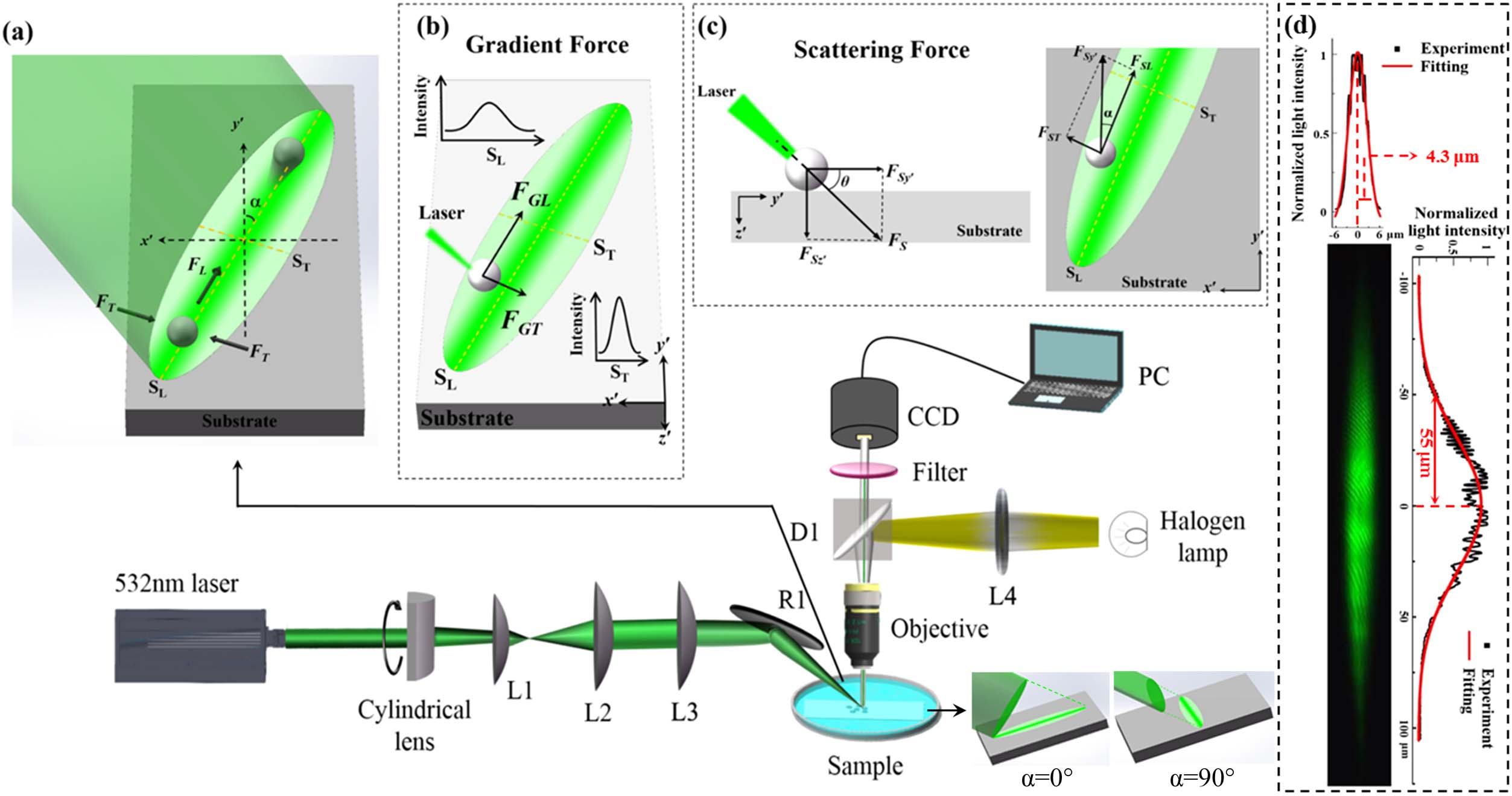
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Department of Cell Biology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510, USA
4 e-mail: thzhechen@jnu.edu.cn
Opto-conveyors have attracted widespread interest in various fields because of their non-invasive and non-contact delivery of micro/nanoparticles. However, the flexible control of the delivery distance and the dynamic steering of the delivery direction, although very desirable in all-optical manipulation, have not yet been achieved by opto-conveyors. Here, using a simple and cost-effective scheme of an elliptically focused laser beam obliquely irradiated on a substrate, a direction-steerable and distance-controllable opto-conveyor for the targeting delivery of microparticles is implemented. Theoretically, in the proposed scheme of the opto-conveyor, the transverse and longitudinal resultant forces of the optical gradient force and the optical scattering force result in the transverse confinement and the longitudinal transportation of microparticles, respectively. In this study, it is experimentally shown that the proposed opto-conveyor is capable of realizing the targeting delivery for microparticles. Additionally, the delivery distance of microparticles can be flexibly and precisely controlled by simply adjusting the irradiation time. By simply rotating the cylindrical lens, the proposed opto-conveyor is capable of steering the delivery direction flexibly within a large range of azimuthal angles, from to 75°. This study also successfully demonstrated the real-time dynamic steering of the delivery direction from to 45° with the dynamical rotation of the cylindrical lens. Owing to its simplicity, flexibility, and controllability, the proposed method is capable of creating new opportunities in bioassays as well as in drug delivery.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001124
上海电力大学 自动化工程学院, 上海 200090
针对低速率解调仪采样获得光纤布喇格光栅反射光谱解调精度低的缺点, 采用了一种基于小波变换的高斯(WTG)曲线拟合方法。利用小波变换对反射光谱信号进行分解, 对小波细节分量进行阈值量化处理, 在此基础上, 运用处理后的细节分量和近似分量对信号进行重构; 然后对重构后的信号插值并进行高斯曲线拟合, 使用Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)算法优化高斯拟合系数。仿真实验结果表明: 与直接寻峰算法、高斯拟合算法相比, WTG算法的峰值定位误差最小, 解调精度更高。
光纤布喇格光栅 小波变换 峰值定位 LM算法 高斯拟合 fiber Bragg grating wavelet transform peak positioning Levenberg-Marquardt algorithms Gauss fitting
湖南航天环宇通信科技股份有限公司, 湖南 长沙 410205
精密光学元件在加工过程中如果工艺控制不当, 产生的划痕、麻点等疵病分布范围虽然较小, 但对整个光学系统的性能影响却很大, 破坏力非常强, 目前的表面疵病检测仪基本上针对平面或球面光学元件进行离线检测。文章以光学加工机床为运动平台, 采用暗场散射成像方法, 设计多光束均匀照明系统, 研究表面疵病微细特征的识别算法, 实现大口径光学表面疵病的在位检测与评价; 标定结果表明, 表面疵病宽度偏差为2.05%, 长度偏差为2.39%, 满足指标要求; 在此基础上针对Φ280 mm平面硅镜进行自动化在位检测, 给出了不同类型疵病的统计数据, 解决了离线检测中非加工时间长与多次装夹引起定位误差等问题。
光学元件 表面疵病 散射成像 在位检测 图像处理 optical elements surface defects scattering imaging In situ detection image processing
暨南大学 理工学院 广州市可见光通信重点实验室,广东 广州 510632
针对单幅图像进行了无透镜显微成像的重构算法研究,介绍了无透镜显微成像系统实验装置和ASM(angle spectrum method)、改编后的L-R(Lucy-Richardson)两种重构算法。对比两种算法重构后的USAF分辨率板图像的分辨率,利用瑞利判据得出ASM获得的振幅图分辨率最高(即3.10 μm),且计算用时最少(即0.9 s),证明了ASM为最佳的单幅无透镜显微重构算法。其次,利用无透镜显微成像系统结合ASM重构的方法,进行细胞成像实验。该无透镜成像视场为5×显微镜的4.4倍,且分辨率介于5×及10×光学显微镜之间,统计学优势明显,在生物医学领域具有广阔的应用前景。
无透镜显微成像 L-R算法 ASM算法 单幅图像重构 lensless microscopic imaging L-R algorithm ASM algorithm reconstruction of single image
1 长春理工大学 理学院, 吉林 长春 130022
2 中国计量科学研究院热工所, 北京 100029
傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)光谱响应度的标定工作是FTIR红外光谱精准测量的基础。基于中国计量科学研究院(NIM)的ThermoGage HT9500型高温基准黑体辐射源, 对NIM搭建的FTIR高温黑体红外辐射特性测量系统的光谱响应度, 通过分段线性标定法进行了标定实验。建立并描述了FTIR测量高温黑体红外辐射特性系统响应度函数标定模型, 并通过测量的黑体辐射源在1 273~1 973 K温区、1~14 μm宽频谱内的红外光谱, 对FTIR测量系统的光谱响应度进行了标定实验研究。结果表明: 分段线性标定FTIR红外光谱测量系统方法具有良好可靠性。1 373~1 873 K温区的测量光谱与基于黑体标定的计算光谱在1~14 μm频谱内平均偏差优于1%, 黑体光谱辐射亮度峰值波长上反演得到的黑体计算温度与实际温度偏差优于0.45%。
计量学 响应度标定 傅里叶红外光谱 高温黑体 宽频谱 metrology responsivity calibration FTIR high temperature blackbody wideband spectrum 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(7): 0718002





